这两天忙着深育和某比赛,没什么时间看actf,也就抽出一两个小时做了下韩文题和这个了,由于某些原因令我犯怵,,,,wp就不写了,写一下这个得了。
题目给了个wav,听声音可以明显听出是调制信号的,看一下题目描述
I’ve bought the second commercial modem for computers in a big city of the UK.
激情澎湃的球迷迷恋这个地方。遇上球赛季,酒吧里的热情、呐喊、啤酒、摇滚,足球 让这个城市充满活力和希望。
从三万英尺的云端望去,往日的生活成了一个遥远微小的地图。
阳光明媚的日子,开始出发,北京时间00:50 开始起飞,一个梦的距离,就可以到达荷 兰阿姆斯特丹,短暂停留之后,然后转机飞往英国
南航的飞机配置完备,全程可以充电,还有wifi,影视屏有面前最新的电影。睡睡醒醒 ,在飞机上觅到一部《北京爱情故事》,让我在三万英尺的空中哭的稀里哗啦。莫名其妙,只能说很套题了😥
文件拿到手直接扔matlab简单处理一首
![图片[1]-ACTF 2022 FFSK WRITEUP-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/image-27-1024x638.png)
看得出来信号频谱还是有点东西的,这里也还是看眼第一个描述吧, second commercial modem for computers
![图片[2]-ACTF 2022 FFSK WRITEUP-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/image-29-1024x460.png)
还是能搜到相关东西的,大概是现成轮子了。章
查阅了相关文章,大概掌握了调制解调编码原理后,写个python脚本来处理一下好了
from scipy.io import wavfile
from goertzel import goertzel
import sys
SAMPLING_RATE = 48000
MARK_TARGET_FREQUENCY = 2225
SPACE_TARGET_FREQUENCY = 2025
SAMPLING_SIZE = 160
def split(l):
temp = []
final_list = []
for item in l:
temp.append(item)
if len(temp) == 160:
final_list.append(temp)
temp = []
return final_list
if __name__ == '__main__':
fs, data = None, None
fs, data = wavfile.read('modem.wav')
full_list_of_samples = list(split(data))
binary_list = ''
decoded_message = ''
for sample in full_list_of_samples:
space = goertzel(sample, SAMPLING_RATE, SPACE_TARGET_FREQUENCY, SAMPLING_SIZE)
mark = goertzel(sample, SAMPLING_RATE, MARK_TARGET_FREQUENCY, SAMPLING_SIZE)
if mark > space:
binary_list += '1'
else:
binary_list += '0'
full_binary_list = [binary_list[i:i + 10] for i in range(0, len(binary_list), 10)]
for each in full_binary_list:
decoded_message += chr(int(each[1:9][::-1], 2))
print decoded_message
![图片[3]-ACTF 2022 FFSK WRITEUP-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/image-30-1024x132.png)
那还真是迷惑,提示了汉明,其他的不用管了
之前运算的时候得知他总共有53640块,根据括号内的20,猜测块的大小是20,啧,整除还是能弄开的,这样就好说了,还是现成轮子,,,
先把上述结果的二进制全部弄出来,网上抄个汉明码的脚本
#### DANIEL MUTHAMA
option=int(input('Press 1 for generating hamming code \nPress 2 for finding error in hamming code\n\t Enter your choice:--\n'))
if(option==1): # GENERATE HAMMING CODE
print('Enter the data bits')
d=input()
data=list(d)
data.reverse()
c,ch,j,r,h=0,0,0,0,[]
while ((len(d)+r+1)>(pow(2,r))):
r=r+1
for i in range(0,(r+len(data))):
p=(2**c)
if(p==(i+1)):
h.append(0)
c=c+1
else:
h.append(int(data[j]))
j=j+1
for parity in range(0,(len(h))):
ph=(2**ch)
if(ph==(parity+1)):
startIndex=ph-1
i=startIndex
toXor=[]
while(i<len(h)):
block=20
toXor.extend(block)
i+=2*ph
for z in range(1,len(toXor)):
h[startIndex]=h[startIndex]^toXor[z]
ch+=1
h.reverse()
print('Hamming code generated would be:- ', end="")
print(int(''.join(map(str, h))))
elif(option==2): # DETECT ERROR IN RECEIVED HAMMING CODE
print('Enter the hamming code received')
d=input()
data=list(d)
data.reverse()
c,ch,j,r,error,h,parity_list,h_copy=0,0,0,0,0,[],[],[]
for k in range(0,len(data)):
p=(2**c)
h.append(int(data[k]))
h_copy.append(data[k])
if(p==(k+1)):
c=c+1
for parity in range(0,(len(h))):
ph=(2**ch)
if(ph==(parity+1)):
startIndex=ph-1
i=startIndex
toXor=[]
while(i<len(h)):
block=20
toXor.extend(block)
i+=2*ph
for z in range(1,len(toXor)):
h[startIndex]=h[startIndex]^toXor[z]
parity_list.append(h[parity])
ch+=1
parity_list.reverse()
error=sum(int(parity_list) * (2 ** i) for i, parity_list in enumerate(parity_list[::-1]))
if((error)==0):
print('There is no error in the hamming code received')
elif((error)>=len(h_copy)):
print('Error cannot be detected')
else:
print('Error is in',error,'bit')
if(h_copy[error-1]=='0'):
h_copy[error-1]='1'
elif(h_copy[error-1]=='1'):
h_copy[error-1]='0'
print('After correction hamming code is:- ')
h_copy.reverse()
print(int(''.join(map(str, h_copy))))
else:
print('Option entered does not exist')
将其hamming等纠错码删除后获得了一串新的01二进制码。
![图片[4]-ACTF 2022 FFSK WRITEUP-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/image-31-1024x276.png)
然而直接转换是转不动的,这里也是简单观察了一波,发现每个十个字符都会有1作为开头0作为结尾,假设这两个为头尾,那么掐头去尾正好是八个字符,正好符合ascii码
处理一下,直接转换,然后发现不行,观察了一下,按位反转,就可以拿到一个base64的内容了。
![图片[5]-ACTF 2022 FFSK WRITEUP-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/image-32-1024x790.png)
最后转一下图片扫码即可
![图片[6]-ACTF 2022 FFSK WRITEUP-魔法少女雪殇](https://cdn.snowywar.top/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/image-33-1024x610.png)
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END



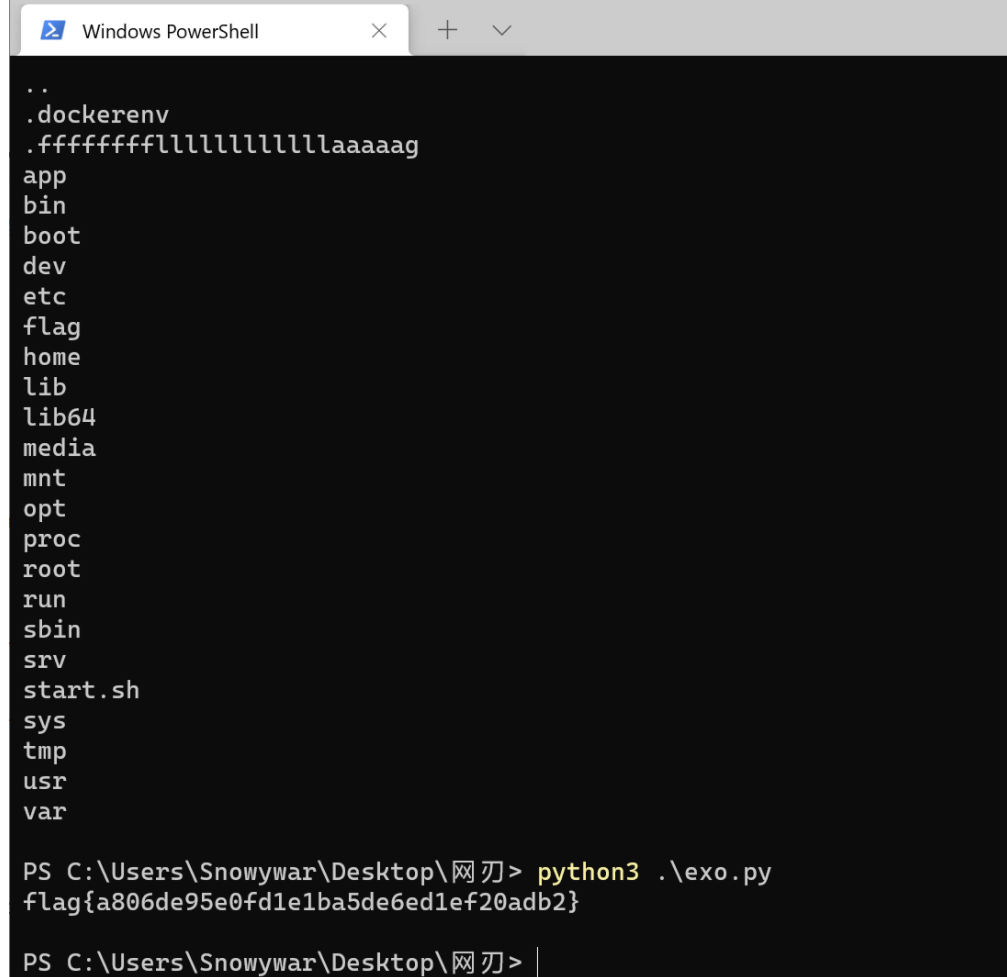
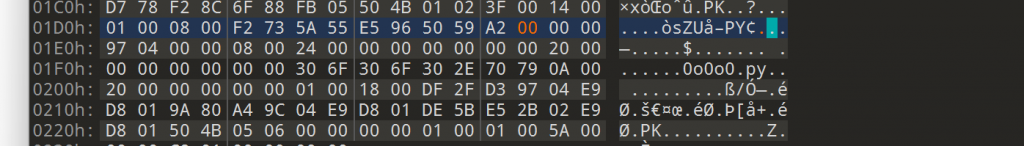






暂无评论内容